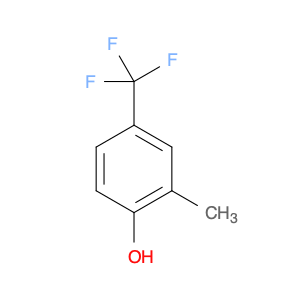
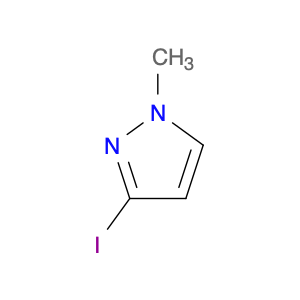
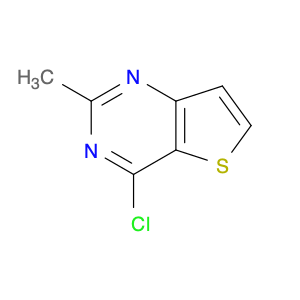
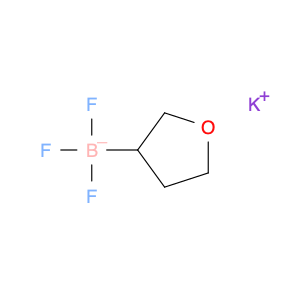
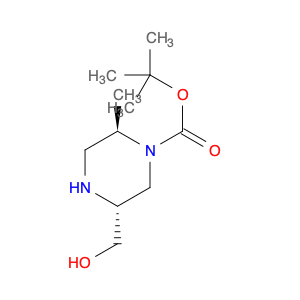
2-Methyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenol, commonly known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely utilized in chemical synthesis for its unique properties and reactivity. In organic synthesis, $name$ serves as a valuable building block due to its ability to undergo various chemical reactions, such as nucleophilic substitutions, acylations, and oxidations. Its trifluoromethyl group enhances the compound's stability and lipophilicity, making it suitable for reactions requiring electron-withdrawing substituents.$name$ is often used as a synthetic intermediate in the pharmaceutical industry for the production of biologically active compounds. Its presence can impart desirable pharmacological properties to drug molecules, such as increased metabolic stability or enhanced binding affinity to target receptors.Furthermore, $name$ is a key component in the preparation of specialty chemicals, agrochemicals, and materials with specific properties. Its versatility in forming diverse chemical bonds makes it a valuable tool for synthetic chemists aiming to create complex molecular structures.Overall, the application of 2-Methyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenol in chemical synthesis showcases its significance in the development of innovative compounds across various industries.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com