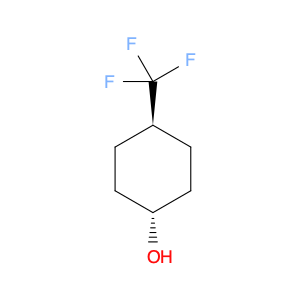
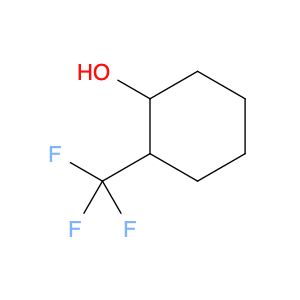
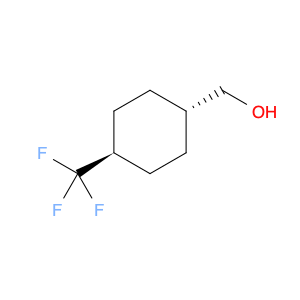
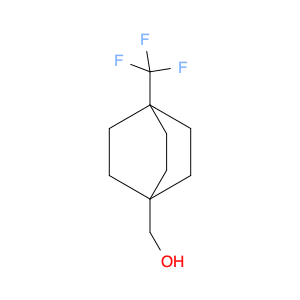
Trans-4-(Trifluoromethyl)cyclohexanol, also known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. Its unique molecular structure consisting of a cyclohexane ring with a trifluoromethyl group at the 4-position imparts distinct reactivity and properties that make it a valuable building block in organic chemistry.One common application of trans-4-(Trifluoromethyl)cyclohexanol in chemical synthesis is as a precursor for the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. The trifluoromethyl group is known to enhance the bioactivity and metabolic stability of molecular compounds, making it a desirable functional group in drug design. By strategically incorporating trans-4-(Trifluoromethyl)cyclohexanol into the synthesis of key intermediates, chemists can access a range of bioactive molecules with improved pharmacokinetic properties.Furthermore, trans-4-(Trifluoromethyl)cyclohexanol can serve as a chiral source in asymmetric synthesis. Its chiral center at the cyclohexane ring allows for the creation of enantiopure compounds, which are crucial in the development of pharmaceuticals and other fine chemicals. Through selective derivatization or transformation of trans-4-(Trifluoromethyl)cyclohexanol, chemists can access enantiomerically pure building blocks for the construction of complex molecular structures.Overall, trans-4-(Trifluoromethyl)cyclohexanol plays a significant role in the field of chemical synthesis, enabling the efficient and versatile preparation of diverse compounds with applications in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com