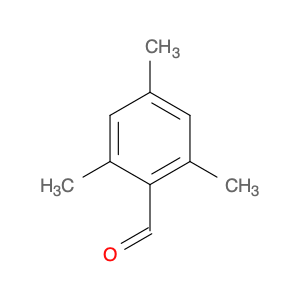
2,5-Dimethyl-1,4-benzenedicarboxaldehyde, also known as $name$, plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis due to its versatile reactivity and unique structural properties. In the realm of organic chemistry, this compound is commonly used as a key intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals.One of the primary applications of $name$ is as a building block in the production of dyes and pigments. Its aromatic structure and functional groups allow for facile reactions with other compounds to yield vibrant and stable colorants. Moreover, the presence of two methyl groups enhances the solubility and stability of the final product, making it a preferred choice in the dye industry.Furthermore, 2,5-Dimethyl-1,4-benzenedicarboxaldehyde is extensively employed in medicinal chemistry for the synthesis of biologically active compounds. By introducing specific substituents to the aldehyde groups, researchers can tailor the molecular structure to exhibit desired pharmacological properties. This compound serves as a valuable starting material for the development of novel drugs targeting various diseases and disorders.Additionally, $name$ is utilized in the preparation of specialty polymers and resins. Its reactive aldehyde groups enable cross-linking reactions with polymers, leading to the formation of durable and high-performance materials. These polymers find applications in coatings, adhesives, and composites, where chemical stability and mechanical strength are paramount.Overall, the application of 2,5-Dimethyl-1,4-benzenedicarboxaldehyde in chemical synthesis spans across multiple industries, showcasing its significance as a versatile building block in organic chemistry.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com