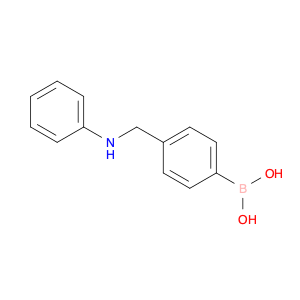
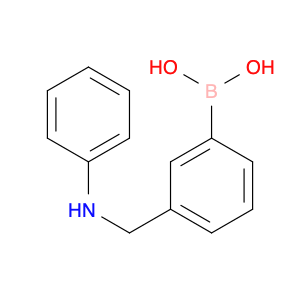
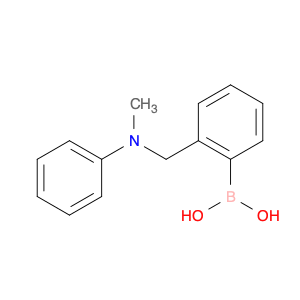
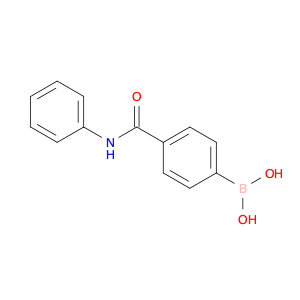
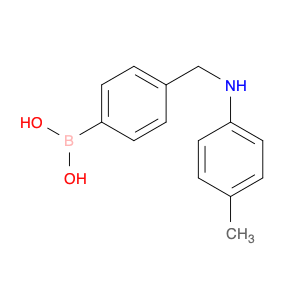
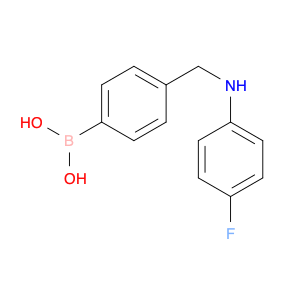
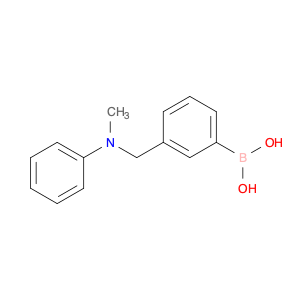
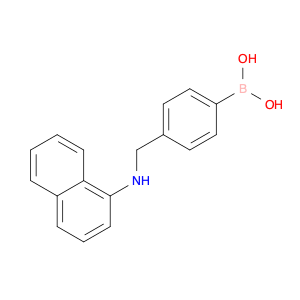
The compound (4-((Phenylamino)methyl)phenyl)boronic acid, also known as $name$, is a versatile reagent commonly used in chemical synthesis. Its primary application lies in the field of organic chemistry, specifically in cross-coupling reactions. $name$ is utilized as a key building block in the synthesis of various organic compounds due to its ability to undergo Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. This reaction involves the coupling of an arylboronic acid with an organic halide or pseudohalide in the presence of a palladium catalyst to form a new carbon-carbon bond. By incorporating $name$ into a synthetic route, chemists can access a wide range of biaryl structures, which are prevalent in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. The simplicity, efficiency, and mild reaction conditions of the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling make $name$ an invaluable tool for the construction of complex molecules in both academic and industrial settings.Moreover, $name$ can be functionalized with various substituents to fine-tune its reactivity and selectivity in cross-coupling reactions, offering chemists a high degree of control over the synthetic outcome. The versatility and reliability of $name$ make it a fundamental reagent for modern organic synthesis strategies, facilitating the efficient creation of diverse molecular architectures with synthetic precision.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com