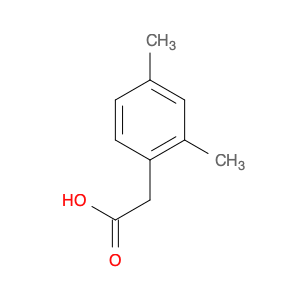
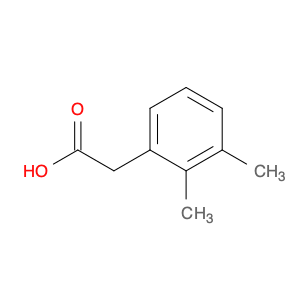
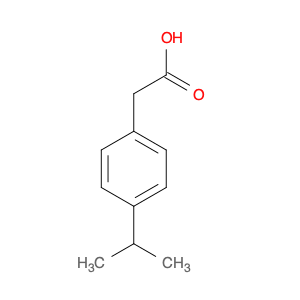
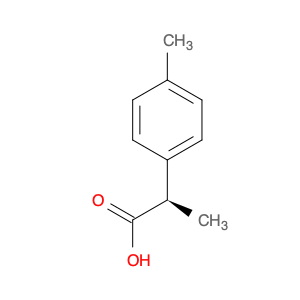
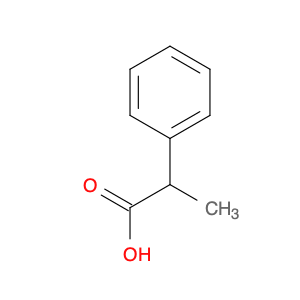
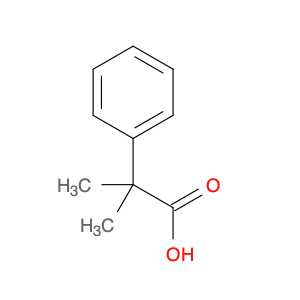
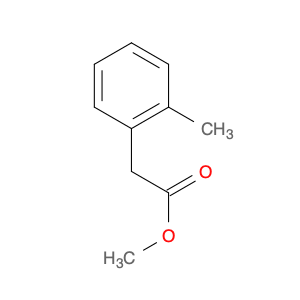
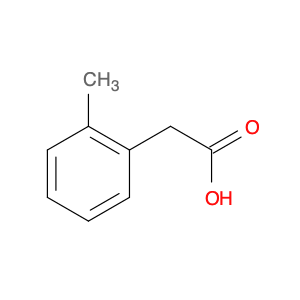
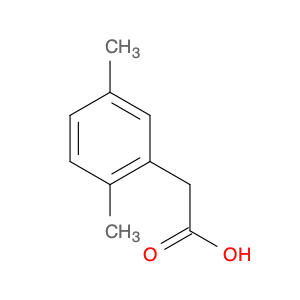
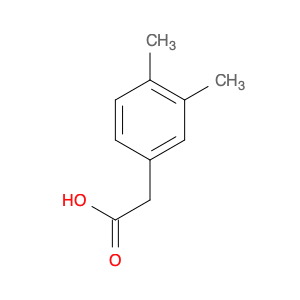
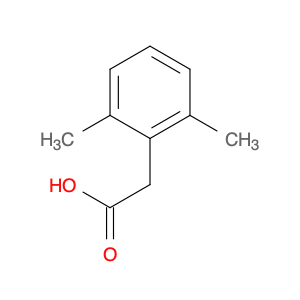
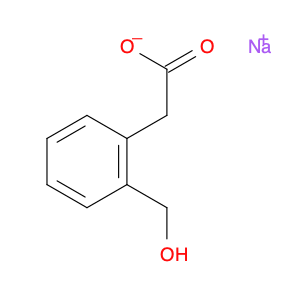
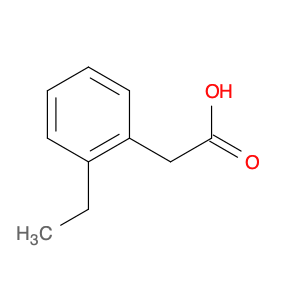
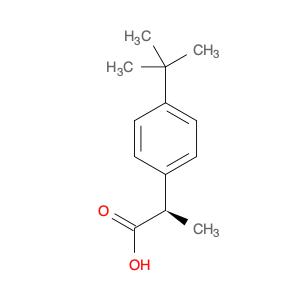
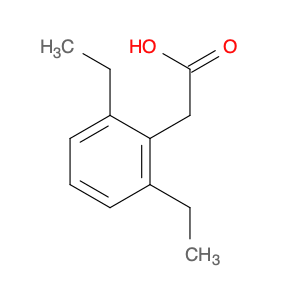
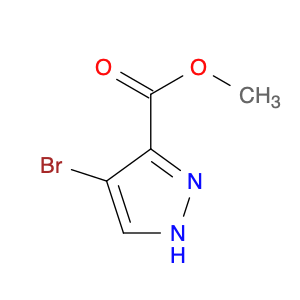
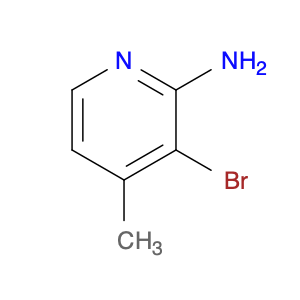
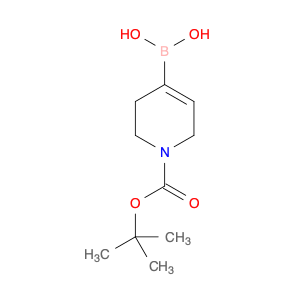
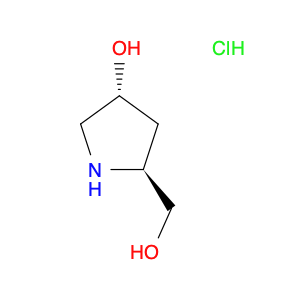
2,4-Dimethylphenylacetic Acid, also known as DMPAA, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. Its application in organic chemistry is crucial for the production of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals. Due to its unique structure and properties, DMPAA serves as a key building block in the synthesis of complex molecules.In chemical synthesis, 2,4-Dimethylphenylacetic Acid is commonly employed as a starting material or intermediate in the preparation of diverse compounds. Its methyl groups provide steric hindrance, influencing the reactivity of the molecule and directing its participation in specific reactions. This enables chemists to control the formation of desired products with high selectivity.One prominent application of 2,4-Dimethylphenylacetic Acid is in the synthesis of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen. By incorporating DMPAA into the chemical pathway, chemists can efficiently generate these important pharmaceuticals on a large scale. Additionally, DMPAA is utilized in the synthesis of herbicides, fragrances, and other specialty chemicals, showcasing its versatility in various industries.Overall, 2,4-Dimethylphenylacetic Acid plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis by enabling the construction of complex molecules with specific functionalities. Its applications extend across pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other chemical sectors, highlighting its significance in the field of organic chemistry.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com