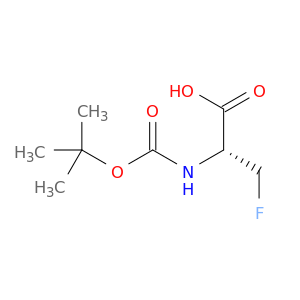
N-[(1,1-Dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-3-fluoro-L-alanine, often referred to as $name$, is a valuable compound widely used in chemical synthesis due to its unique properties and versatile applications. This compound serves as a key building block in the creation of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials with specific structural and functional requirements.In chemical synthesis, $name$ acts as a crucial intermediate in the preparation of various complex molecules and fine chemicals. Its functional groups and stereochemistry make it a favored choice for introducing specific structural motifs and enhancing the overall efficiency of multi-step synthetic pathways.Specifically, $name$ is frequently utilized in peptide synthesis, where its protective group properties play a critical role in controlling the regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of reactions. By selectively masking reactive functional groups, such as amines or carboxylic acids, $name$ enables the sequential assembly of peptide chains with high purity and yield.Furthermore, the introduction of the fluoro substituent in 3-fluoro-L-alanine imparts unique physicochemical properties to the final products, potentially enhancing bioactivity or metabolic stability in pharmaceutical compounds. This modification can also facilitate the development of fluorinated organic materials with advanced properties for a wide range of industrial applications.In summary, the strategic incorporation of N-[(1,1-Dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-3-fluoro-L-alanine into synthetic routes offers chemists a powerful tool for designing and accessing structurally diverse and functionally enhanced molecules in both laboratory research and industrial production settings.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com