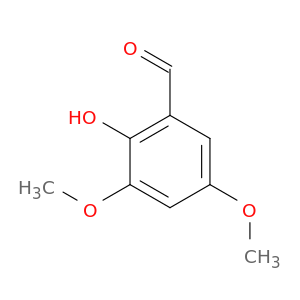
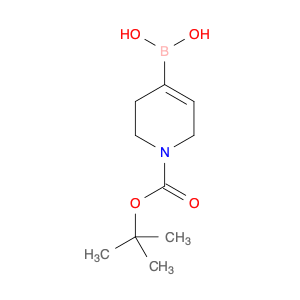
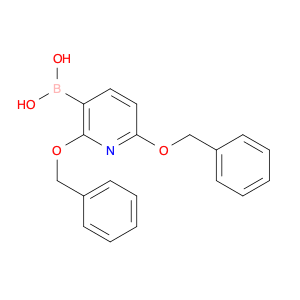
2-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde, also known as $name$, is a key compound widely utilized in chemical synthesis due to its versatile reactivity and unique properties. In the realm of organic chemistry, this compound serves as a crucial building block for the preparation of various complex molecules and pharmaceuticals. Its hydroxyl and methoxy groups enable it to participate in a range of reactions, making it a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of diverse organic compounds.One significant application of 2-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde is its role in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds. By undergoing condensation reactions with amines or other nucleophiles, this compound can be used to generate important heterocycles such as benzoxazoles and benzimidazoles. These heterocyclic structures are found in numerous biologically active molecules and pharmaceuticals, highlighting the importance of 2-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde in drug discovery and development.Furthermore, the aldehyde functionality of 2-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde makes it a valuable precursor for the synthesis of various aromatic compounds. Through selective reduction or oxidation reactions, this compound can be transformed into different alcohols or carboxylic acids, expanding its utility in the preparation of a wide range of organic molecules.In summary, 2-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis, particularly in the construction of heterocyclic compounds and aromatic derivatives. Its versatile reactivity and ability to serve as a key intermediate make it a valuable tool for organic chemists engaged in the design and synthesis of novel compounds and pharmaceuticals.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com