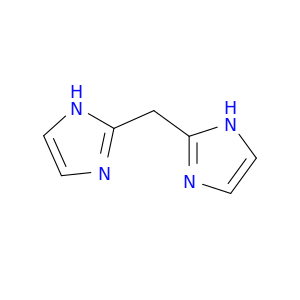
Di(1H-imidazol-2-yl)methane, also known as DIBM, is a versatile compound widely utilized in chemical synthesis as a powerful ligand in coordination chemistry. Its unique structure featuring two imidazole rings attached to a central methane unit imparts various interesting properties that make it invaluable in numerous synthetic applications.In chemical synthesis, Di(1H-imidazol-2-yl)methane serves as a key ligand in transition metal catalyzed reactions, particularly in the formation of metal-organic complexes. Due to its ability to coordinate with metal ions, DIBM plays a crucial role in facilitating a wide range of catalytic processes, including cross-coupling reactions, C-H activation, and asymmetric catalysis. Its coordination chemistry also enables the stabilization of reactive intermediates and influences the regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of the reactions.Moreover, Di(1H-imidazol-2-yl)methane demonstrates chelating properties, allowing it to form stable complexes with various transition metals such as copper, palladium, and nickel. These complexes exhibit enhanced catalytic activity and selectivity, making DIBM a popular choice for designing efficient and sustainable synthetic routes in organic chemistry.Overall, the application of Di(1H-imidazol-2-yl)methane in chemical synthesis showcases its significance as a versatile ligand that enables the development of new methodologies and strategies for the construction of complex organic molecules with high efficiency and precision.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com