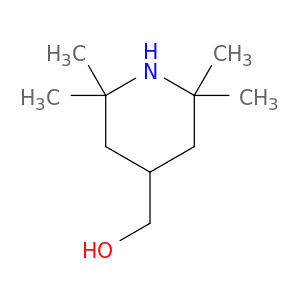
The compound (2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidin-4-yl)methanol, also known as $name$, is a versatile reagent widely used in chemical synthesis processes. Its primary application lies in its function as a sterically hindered alcohol, which enables it to act as a powerful inhibitor in various reactions.In chemical synthesis, $name$ is often employed as a robust radical scavenger and stabilizer, particularly in polymerization reactions. Its unique molecular structure confers excellent stability and reactivity, making it an ideal choice for controlling radical polymerization processes.Additionally, $name$ is frequently utilized in the synthesis of complex organic compounds and pharmaceutical intermediates. Its sterically hindered nature plays a key role in enhancing selectivity and controlling reaction kinetics, leading to improved yields and higher product purity.Overall, the use of $name$ in chemical synthesis offers precise control over reaction pathways, allowing for the efficient and reliable production of a wide range of chemicals and materials.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com