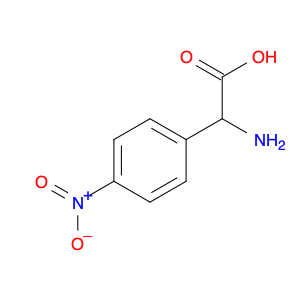
2-Amino-2-(4-nitrophenyl)acetic acid, also known as ANPA, is a versatile compound widely utilized in chemical synthesis due to its unique properties and reactivity. This compound plays a critical role in the development of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and advanced materials.In chemical synthesis, 2-Amino-2-(4-nitrophenyl)acetic acid serves as a key building block for the construction of complex organic molecules. Its amino and nitro functional groups provide opportunities for diverse reactions, making it valuable in the formation of new chemical entities. ANPA can be readily modified through various chemical manipulations, allowing for the introduction of different functional groups and structural motifs.One of the primary applications of 2-Amino-2-(4-nitrophenyl)acetic acid is in the synthesis of peptide-based compounds. Peptides are essential biomolecules with numerous biological activities, and ANPA can act as a precursor for the incorporation of amino acids into peptide chains. By coupling ANPA with other amino acids, researchers can create custom peptides with specific sequences and properties for use in drug discovery and biochemical studies.Additionally, 2-Amino-2-(4-nitrophenyl)acetic acid can participate in various transformations such as nucleophilic substitution, reduction, and condensation reactions. These reactions enable the formation of diverse chemical structures, making ANPA an indispensable tool for organic chemists striving to access novel compounds with tailored functions.Overall, the application of 2-Amino-2-(4-nitrophenyl)acetic acid in chemical synthesis offers researchers a versatile and efficient route to the development of complex molecules with potential applications across multiple scientific fields.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com