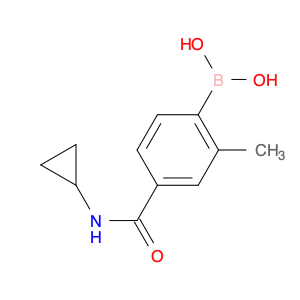
The (4-(Cyclopropylcarbamoyl)-2-methylphenyl)boronic acid, also known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. This boronic acid derivative plays a crucial role as a building block in organic chemistry reactions, particularly in the formation of carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom bonds. $name$ is commonly employed as a key reagent in Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions, a powerful method utilized for the construction of biaryl compounds. This reaction, catalyzed by a palladium complex, involves the coupling of an aryl or heteroaryl boronic acid with an aryl or heteroaryl halide or pseudohalide to form the desired biaryl product. The presence of the cyclopropylcarbamoyl and methylphenyl groups in $name$ enhances the reactivity and selectivity of the boronic acid, making it a valuable tool for the synthesis of complex organic molecules.Furthermore, $name$ can also be utilized in the preparation of diverse pharmaceutical intermediates, agrochemicals, and materials science applications due to its ability to participate in various functional group transformations and complex molecule assembly. Its unique structural features make it an indispensable component in the toolbox of synthetic chemists working in drug discovery, materials development, and other fields requiring precise and efficient organic synthesis strategies.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com