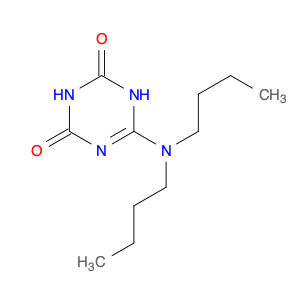
1,3,5-Triazine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, 6-(dibutylamino)-, commonly known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. This compound plays a crucial role in various reactions and processes within the field of chemistry.One of the primary applications of $name$ in chemical synthesis is its use as a reagent in organic reactions. Due to its unique chemical structure and properties, it serves as an effective catalyst in a range of synthetic transformations. Specifically, $name$ can act as a powerful nucleophile in nucleophilic addition reactions, facilitating the creation of new chemical bonds and the formation of complex molecules.Moreover, $name$ is frequently employed as a building block in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds. Its ability to participate in multiple types of reactions allows chemists to tailor its reactivity for specific synthetic pathways, enabling the preparation of diverse molecular structures.Furthermore, $name$ is utilized in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials due to its role as a key intermediate in the synthesis of bioactive compounds. Its presence in the molecular structure of these products imparts desired properties and functionalities essential for their intended applications.In conclusion, the significance of 1,3,5-Triazine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione, 6-(dibutylamino)- in chemical synthesis lies in its versatility and utility as a reagent, catalyst, and building block for the creation of valuable compounds across various industries.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com