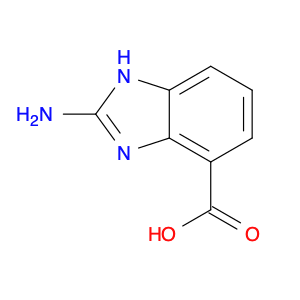
2-Amino-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-4-carboxylic acid, also known as $name$, is a versatile compound commonly used in chemical synthesis for various applications. In organic synthesis, $name$ serves as a key building block for the preparation of various pharmaceuticals and bioactive compounds. Its unique chemical structure allows for the formation of important heterocyclic ring systems, which are essential components in many drug molecules.$name$ is frequently employed in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds, including benzimidazoles, which are important scaffolds in medicinal chemistry. By incorporating $name$ into synthetic routes, chemists can efficiently access diverse molecular structures with potential biological activity. Additionally, $name$ can be utilized as a precursor for the synthesis of complex molecules through various functional group transformations, such as acylations, alkylations, and cyclizations.Furthermore, $name$ plays a crucial role in the development of new synthetic methodologies and strategies. Its involvement in catalytic processes, cross-coupling reactions, and diversity-oriented synthesis strategies broadens its utility in chemical research. Overall, the versatile nature of 2-Amino-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-4-carboxylic acid makes it a valuable tool in the field of chemical synthesis, enabling the efficient construction of diverse molecular architectures with potential applications in drug discovery and materials science.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com