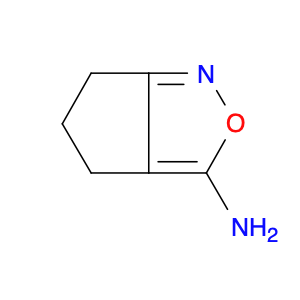
The compound 5,6-Dihydro-4H-cyclopenta[c]isoxazol-3-amine, referred to as $name$, is a versatile building block in chemical synthesis. In organic chemistry, this compound serves as a key intermediate in the construction of various biologically active molecules and pharmaceutical compounds. Its unique structure and reactivity make it a valuable tool for creating complex molecular structures through a series of synthetic transformations.One common application of $name$ in chemical synthesis is its utility as a precursor in the preparation of heterocyclic compounds. By reacting $name$ with various reagents and catalysts, chemists can efficiently access a wide range of fused heterocycles with diverse pharmacological properties. Furthermore, the presence of the isoxazol ring in the molecule offers opportunities for further functionalization, enabling the introduction of additional substituents or modifications to tailor the compound for specific applications.Additionally, the presence of the amine functional group in 5,6-Dihydro-4H-cyclopenta[c]isoxazol-3-amine provides avenues for selective derivatization and further elaboration, allowing for the introduction of specific functionalities or stereochemical motifs in the final product. This versatility makes $name$ a valuable asset in the repertoire of synthetic chemists seeking to access novel heterocyclic scaffolds for drug discovery or material science applications.In summary, the strategic incorporation of 5,6-Dihydro-4H-cyclopenta[c]isoxazol-3-amine into chemical synthesis pathways enables the efficient construction of diverse molecular architectures with applications in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. Its role as a key building block highlights its importance in facilitating the creation of complex molecules with tailored properties and functions.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com