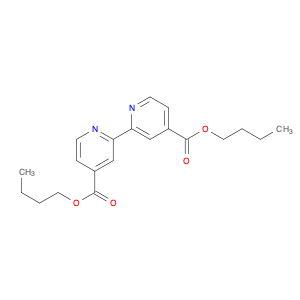
4,4'-Bis(butoxycarbonyl)-2,2'-bipyridine, commonly known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. This compound plays a key role in complex organic reactions, particularly in the field of coordination chemistry and catalysis.In chemical synthesis, $name$ serves as a crucial ligand in transition metal-catalyzed reactions, acting as a chelating agent to stabilize metal complexes and facilitate various transformations. Its unique structure containing bipyridine moieties with butoxycarbonyl functional groups provides a scaffold for controlling the reactivity and selectivity of metal catalysts.One important application of 4,4'-Bis(butoxycarbonyl)-2,2'-bipyridine is in the preparation of coordination complexes for catalytic purposes. By coordinating with transition metals such as palladium or copper, $name$ enables the selective activation of C–H bonds, cross-coupling reactions, and asymmetric catalysis, leading to the formation of intricate organic molecules with high efficiency and precision.Moreover, the presence of butoxycarbonyl groups in $name$ offers protection to sensitive functional groups during chemical transformations, allowing for orthogonality in multi-step synthesis and enhancing the overall synthetic strategy. By judiciously designing ligand–metal combinations involving 4,4'-Bis(butoxycarbonyl)-2,2'-bipyridine, chemists can access novel reactivity pathways and unlock the potential for creating structurally diverse compounds with tailored properties.Overall, the use of 4,4'-Bis(butoxycarbonyl)-2,2'-bipyridine in chemical synthesis showcases its significance as a versatile building block for designing advanced catalyst systems and driving the development of innovative synthetic methodologies.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com