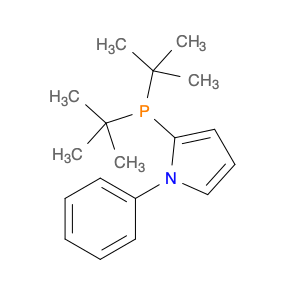
2-(di-tert-Butylphosphino)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrrole, commonly referred to as $name$, is a versatile compound that plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis. This compound serves as a highly effective ligand in transition metal catalysis reactions, particularly in metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions.Due to its unique structural characteristics, $name$ exhibits excellent coordinating abilities with transition metals such as palladium, copper, and nickel. This allows it to facilitate the formation of stable coordination complexes, thereby enhancing the efficiency and selectivity of various catalytic processes.In chemical synthesis, the application of $name$ as a ligand has been documented in a wide range of transformations, including but not limited to Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions, Heck reactions, and Buchwald-Hartwig amination reactions. Its ability to stabilize metal catalysts and regulate their reactivity makes it a valuable tool for forming C-C and C-N bonds, essential steps in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials.Moreover, the steric bulkiness imparted by the di-tert-butylphosphino group in $name$ plays a crucial role in controlling the regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of the catalytic transformations, leading to the formation of desired compounds with high yields and minimal byproducts.Overall, the use of 2-(di-tert-Butylphosphino)-1-phenyl-1H-pyrrole in chemical synthesis represents a significant advancement in the field of catalysis, offering chemists a powerful tool to achieve complex molecule synthesis with precision and efficiency.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com