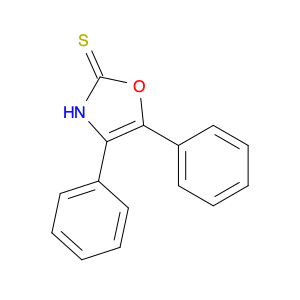
4,5-Diphenyloxazole-2(3H)-thione, also known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely utilized in chemical synthesis for its unique properties and reactivity. In the realm of organic chemistry, $name$ serves as a key building block for the construction of various complex molecules and functional materials.One of the primary applications of 4,5-Diphenyloxazole-2(3H)-thione in chemical synthesis is its role as a valuable heterocyclic scaffold. This compound's heterocyclic structure containing both oxygen and sulfur atoms makes it particularly useful for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other biologically active compounds. By incorporating $name$ into the molecular structure, chemists can introduce desirable properties and functionalities, enhancing the overall potency and selectivity of the target molecule.Furthermore, 4,5-Diphenyloxazole-2(3H)-thione exhibits interesting photophysical properties, making it a promising candidate for applications in materials science and optoelectronics. Its ability to absorb and emit light at specific wavelengths makes it suitable for the development of fluorescent probes, sensors, and organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). The inclusion of $name$ in the design of such materials can lead to enhanced performance and efficiency, expanding the possibilities for advanced technological applications.Overall, the diverse applications of 4,5-Diphenyloxazole-2(3H)-thione in chemical synthesis highlight its significance as a versatile and valuable compound in the realm of organic chemistry. Its unique structural features and reactivity make it an indispensable tool for the creation of novel molecules and functional materials with tailored properties and applications.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com