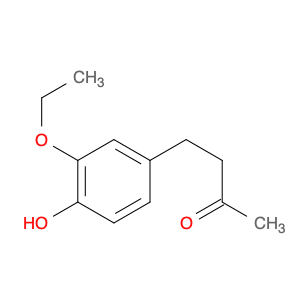
4-(3-Ethoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone, often referred to as $name$, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis for its unique properties and functionalities. This compound serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of various organic compounds, owing to its ability to participate in a range of chemical reactions. In organic synthesis, $name$ is commonly employed as a building block for the preparation of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, fragrances, and other fine chemicals.One of the primary applications of 4-(3-Ethoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone in chemical synthesis is its role as a key precursor in the formation of complex organic molecules. By utilizing the reactive functional groups present in $name$, chemists can manipulate its structure to generate new compounds with tailored properties. Additionally, the presence of both an ethoxy and hydroxy group in the phenyl ring and a butanone moiety provides ample opportunities for derivatization, enabling the synthesis of diverse chemical entities.Moreover, the unique structural features of 4-(3-Ethoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone make it an attractive candidate for the construction of biologically active molecules. The combined presence of an ethoxy group and a hydroxy group in the aromatic ring confers specific chemical reactivity that can be leveraged to introduce desired functional groups into the molecule. This versatility allows for the design and synthesis of novel compounds with potential applications in pharmaceutical development, medicinal chemistry, and materials science.Overall, the strategic incorporation of 4-(3-Ethoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone in chemical synthesis enables chemists to access a diverse array of compounds with tailored properties and functionalities. By harnessing the synthetic potential of this compound, researchers can explore new avenues in drug discovery, material design, and other areas of chemical research.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com