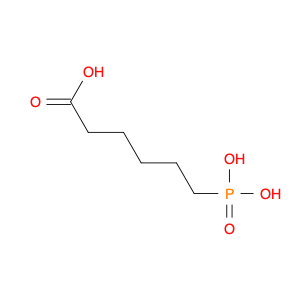
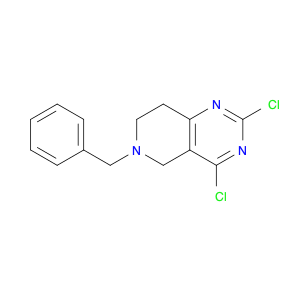
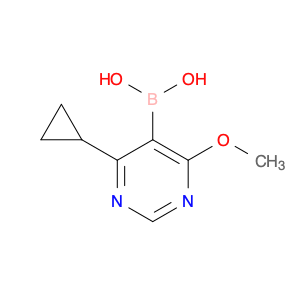
6-Phosphonohexanoic acid, also known as P6A, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. This unique molecule serves as a key building block in the creation of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials due to its distinct chemical properties. In organic synthesis, 6-Phosphonohexanoic acid acts as a crucial intermediate in the production of a wide range of organic compounds, serving as a precursor for the synthesis of biologically active molecules and polymers.Its ability to undergo various chemical reactions, such as esterification, amidation, and condensation, makes it a valuable component in the development of novel compounds. One of the key applications of 6-Phosphonohexanoic acid is in the formation of peptide bonds, essential for peptide synthesis and the production of peptides with specific biological activities. Additionally, its role as a phosphorylating agent enables the introduction of phosphonate functionalities into organic molecules, expanding the scope of chemical diversity achievable in synthesis.Moreover, 6-Phosphonohexanoic acid's unique structural features and reactivity make it a useful tool in medicinal chemistry for drug discovery and development. By incorporating this compound into molecular scaffolds, chemists can modify the properties of potential drug candidates to enhance their efficacy and bioavailability. Overall, the application of 6-Phosphonohexanoic acid in chemical synthesis plays a crucial role in advancing scientific research and innovation across various industries.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com