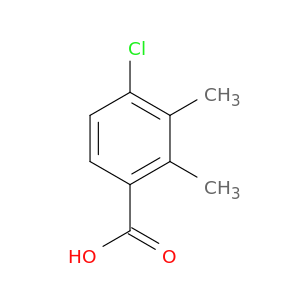
4-Chloro-2,3-dimethylbenzoic acid, also known as $name$, serves a crucial role in chemical synthesis as a versatile building block. This compound is commonly utilized in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. Its unique structure enables it to participate in a wide range of reactions, making it a valuable precursor in the production of diverse compounds.In chemical synthesis, 4-Chloro-2,3-dimethylbenzoic acid can undergo reactions such as esterification, amidation, and halogenation to introduce specific functional groups to the molecule. These functionalized derivatives can then be further modified to create complex structures with enhanced properties for specific applications. Additionally, the presence of the chloro group provides opportunities for selective transformations, enabling chemists to control the regioselectivity and stereochemistry of the final products.Overall, the application of 4-Chloro-2,3-dimethylbenzoic acid in chemical synthesis highlights its importance as a key intermediate in the development of valuable compounds across various industries. Its versatility and reactivity make it a valuable tool for organic chemists seeking to design and create new molecules with targeted properties and functions.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com