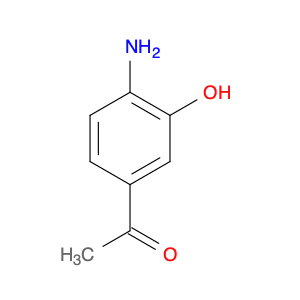
1-(4-Amino-3-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone, also known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. With its unique chemical structure, this compound plays a crucial role in the development of various pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and organic compounds.In chemical synthesis, $name$ serves as a key intermediate in the production of numerous important molecules. Its ability to undergo various reactions, such as acylation, alkylation, and condensation, makes it a valuable building block for the creation of complex organic compounds. Additionally, the presence of both an amino group and a hydroxy group in its structure allows for further functionalization, enabling the incorporation of specific chemical functionalities into the final products.Moreover, the incorporation of $name$ into organic synthesis pathways can lead to the formation of biologically active molecules with potential pharmaceutical applications. Its functional groups provide opportunities for the introduction of specific pharmacophores, enhancing the bioactivity and pharmacokinetic properties of the resulting compounds. This versatility makes $name$ a valuable tool for medicinal chemists and researchers working on drug discovery projects.Furthermore, in the fragrance industry, $name$ can be utilized to synthesize aroma compounds with unique olfactory profiles. By incorporating this compound into fragrance formulations, perfumers can create distinctive scents that cater to specific consumer preferences. The presence of the amino and hydroxy groups in $name$ allows for interactions with other fragrance ingredients, leading to the development of complex and long-lasting fragrances.Overall, the application of 1-(4-Amino-3-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone in chemical synthesis showcases its significance in organic chemistry, pharmaceutical development, and fragrance creation. Its versatility and reactivity make it a valuable component in the toolkit of synthetic chemists and researchers seeking to innovate in various fields.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com