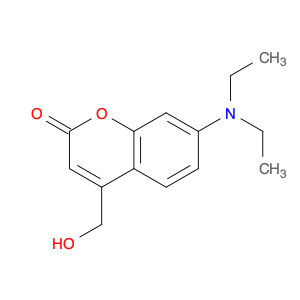
7-(Diethylamino)-4-(hydroxymethyl)-2H-chromen-2-one, also known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis due to its unique properties and reactivity. This compound serves as a valuable building block in the synthesis of various organic molecules, especially in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries.One of the key applications of $name$ in chemical synthesis is its role as a precursor for the synthesis of coumarin derivatives. Coumarins are a class of compounds known for their diverse biological activities, including antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties. By utilizing $name$ as a starting material, chemists can easily modify its chemical structure to introduce different functional groups and create novel coumarin derivatives with enhanced biological activities.Additionally, 7-(Diethylamino)-4-(hydroxymethyl)-2H-chromen-2-one can be used in the synthesis of fluorescent dyes and probes. Its chromophore structure allows for the introduction of fluorescent moieties, making it a valuable tool in chemical biology and bioimaging studies. The ability to tune the fluorescence properties of $name$ derivatives makes them ideal candidates for various analytical and diagnostic applications.Furthermore, $name$ can also be employed as a building block in the construction of heterocyclic compounds and chiral molecules. Its unique structural features and reactivity enable chemists to access a wide range of complex organic structures with defined stereochemistry, making it a valuable resource in synthetic organic chemistry.In conclusion, 7-(Diethylamino)-4-(hydroxymethyl)-2H-chromen-2-one plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis by serving as a versatile intermediate for the preparation of diverse organic compounds with potential applications in drug discovery, materials science, and chemical biology. Its flexibility and reactivity make it an indispensable tool for synthetic chemists seeking to access new chemical space and develop innovative molecules for various industrial and research purposes.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com