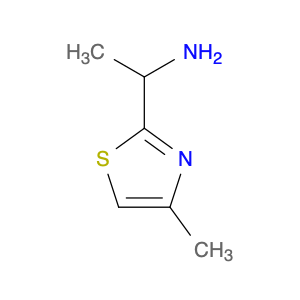
1-(4-Methylthiazol-2-yl)ethanamine, commonly referred to as MTEA, is a versatile compound widely utilized in chemical synthesis for its unique properties and reactivity. This molecule serves as a valuable building block in the creation of various pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals due to its ability to participate in a wide range of organic reactions.In chemical synthesis, MTEA is often employed as a key intermediate in the preparation of complex organic compounds. Its thiazole ring structure and amino group provide opportunities for functional group interconversions, such as acylation, alkylation, and Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. These transformations allow chemists to introduce different chemical moieties onto the MTEA backbone, enabling the generation of structurally diverse and biologically active molecules.Moreover, the unique molecular scaffold of 1-(4-Methylthiazol-2-yl)ethanamine imparts specific pharmacological properties to the final products. By strategically incorporating MTEA into molecular designs, researchers can modulate the compound's bioactivity, bioavailability, and pharmacokinetic profile. This makes MTEA a valuable tool in drug discovery and development, where precise control over molecular structure is essential for optimizing therapeutic efficacy and minimizing potential side effects.Overall, the versatile nature of 1-(4-Methylthiazol-2-yl)ethanamine makes it a valuable asset in the arsenal of synthetic chemists, enabling the construction of complex molecules with tailored properties for various applications across the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com