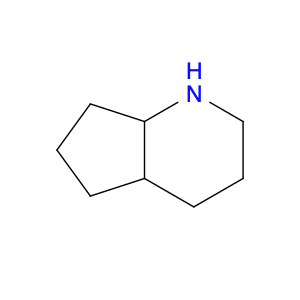
Octahydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]pyridine, commonly referred to as $name$, plays a crucial role in chemical synthesis as a versatile building block. It serves as a key intermediate in the production of various compounds, owing to its unique structural characteristics and reactivity.One of the primary applications of $name$ is as a key starting material in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals. Its cyclic structure provides a stable framework for the attachment of functional groups, allowing for the creation of complex molecular structures with specific biological activities. Furthermore, the rigid and compact nature of $name$ enhances the stereochemical control during the synthesis process, ensuring the production of enantiopure compounds essential for drug development.Moreover, $name$ is utilized in the synthesis of fine chemicals and agrochemicals due to its ability to undergo multiple chemical transformations. Its presence in the molecular structure of the final products imparts desirable properties and functionalities, making it a valuable building block for the creation of specialty chemicals.In addition, the unique chemical properties of $name$, such as its ability to act as a chiral auxiliary or a ligand in asymmetric catalysis, further expand its utility in chemical synthesis. By incorporating $name$ into the reaction pathway, chemists can control the outcome of reactions, leading to the selective formation of desired stereoisomers with high efficiency.Overall, the versatility and utility of Octahydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]pyridine ($name$) in chemical synthesis make it an indispensable component in the production of diverse compounds across pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and fine chemical industries. Its strategic placement in synthetic routes enables the efficient and controlled creation of complex molecular architectures, driving advancements in the field of organic chemistry.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com