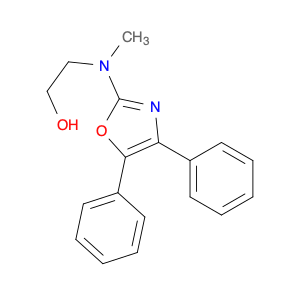
2-((4,5-Diphenyloxazol-2-yl)(methyl)amino)ethanol, also known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis. This molecule plays a crucial role in organic chemistry as a building block for the synthesis of various complex organic compounds. Its unique structure containing an oxazole ring and an amino group makes it a valuable reagent in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science.In chemical synthesis, $name$ is particularly employed as a key intermediate in the preparation of biologically active compounds due to its ability to participate in a range of organic reactions. Its oxazole ring can undergo functionalization processes such as halogenation, alkylation, and acylation, allowing for the introduction of different functional groups into the molecule. The amino group in $name$ also provides versatility in forming amide, ester, or other types of bonds with various organic substrates.Moreover, the presence of both electron-rich and electron-withdrawing groups in $name$ enhances its reactivity towards electrophiles and nucleophiles, facilitating its involvement in diverse synthetic transformations. This compound serves as a valuable tool for medicinal chemists, materials scientists, and other researchers seeking to design and develop new molecules with desired properties.Overall, the application of 2-((4,5-Diphenyloxazol-2-yl)(methyl)amino)ethanol in chemical synthesis showcases its significance as a key component in the creation of innovative organic compounds with potential applications in various fields.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com