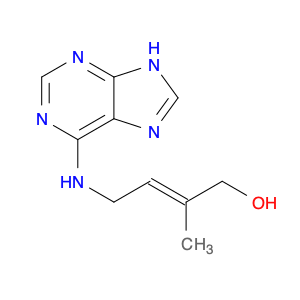
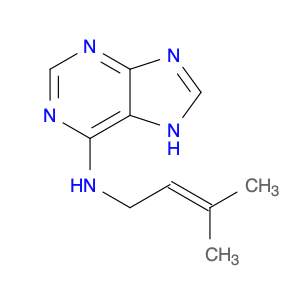
Trans-6-(4-Hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl)amino purine, also known as $name$, is a versatile compound widely used in chemical synthesis as a key intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialized materials. Its unique chemical structure allows for the formation of intricate molecular arrangements, making it an essential building block in organic synthesis processes.In chemical synthesis, $name$ is utilized as a precursor in the creation of various biologically active compounds, such as antiviral drugs and enzyme inhibitors. Its amino purine moiety enables the introduction of functional groups and substitutions at specific positions, providing control over the reactivity and selectivity of the synthesis reactions. Moreover, the presence of the hydroxy and methylbutenyl groups enhances the compound's stability and solubility, facilitating its manipulation in complex chemical reactions.Additionally, the versatile nature of $name$ allows for the modification of its structure through various synthetic routes, leading to the development of novel chemical entities with potential applications in medicinal chemistry, materials science, and biological research. Its role in chemical synthesis embodies its importance in advancing the fields of organic chemistry and pharmaceutical development, showcasing its significance as a valuable tool for generating molecular diversity and complexity.
 sales@aaronchem.com
sales@aaronchem.com